前言
有很多iOS开源项目通过hook第三层转发forwardInvocation,去实现各种各样的黑魔法。如果一个项目工程同时接入了多个这样的库,那么在享受这些库给我们带来便利的同时,也有可能会遭受这些库带来的各种各样的坑。
iOS的消息转发机制
iOS的消息转发机制已经被讲的烂大街了,这里不再赘述,直接画重点,OC方法调用主要遵循以下调用流程:
- 1、先查找类的方法缓存,如果能找到,跳到done;
- 2、重新查找类的方法缓存,如果能找到,跳到done;
- 3、依次遍历类的方法列表,如果能找到,将查找的方法添加到缓存,跳到done;
- 4、循环遍历该类的父类,直到
NSObject,对其中的每一层父类依次执行3和4的操作;- 5、如果当前类和其父类链中均没有找到,进入方法决议,如果决议成功,跳转retry;
- 6、如果方法决议未实现,runtime就会询问当前的接受者是否有其他对象可以处理这个未知的selector,方法是
forwardingTargetForSelector:- 7、如果没有备援接收者,那么进行消息重定向。这个时候runtime会将未知消息的所有细节都封装为NSInvocation对象,调用
forwardInvocation:
iOS消息转发机制的Hook原理
根据上面的消息转发机制:当调用一个OC对象的方法时,会沿着继承链层层往上寻找,直到寻找到NSObject,如果还没有寻找到,说明这个方法不存在,但是并不会马上抛出异常,而是会经过多层转发,层层调用对象的-resolveInstanceMethod:, -forwardingTargetForSelector:, -methodSignatureForSelector:, -forwardInvocation: 等方法。其中最后 -forwardInvocation: 是会有一个 NSInvocation 对象,这个 NSInvocation 对象保存了这个方法调用的所有信息,包括 Selector 名,参数和返回值类型,最重要的是有所有参数值,可以从这个 NSInvocation 对象里拿到调用的所有参数值。
如果我们想实现一个库,来动态修改某些方法的实现,那么就可以利用hookforwardInvocation来实现:自定义一个自己的forwardInvocation处理函数,把要修改的方法的调用统统都通过转发到这个处理函数里面,然后就可以动态控制这些方法的下一步的具体走向了。
(1)JSPatch的Hook原理
先来看下JSPatch是如何来实现的,在JSPatch.mm文件中可以看到overrideMethod的定义1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48static void overrideMethod(Class cls, NSString *selectorName, JSValue *function, BOOL isClassMethod, const char *typeDescription)
{
SEL selector = NSSelectorFromString(selectorName);
if (!typeDescription) {
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(cls, selector);
typeDescription = (char *)method_getTypeEncoding(method);
}
IMP originalImp = class_respondsToSelector(cls, selector) ? class_getMethodImplementation(cls, selector) : NULL;
IMP msgForwardIMP = _objc_msgForward;
if (typeDescription[0] == '{') {
NSMethodSignature *methodSignature = [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:typeDescription];
if ([methodSignature.debugDescription rangeOfString:@"is special struct return? YES"].location != NSNotFound) {
msgForwardIMP = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_stret;
}
}
if (class_getMethodImplementation(cls, @selector(forwardInvocation:)) != (IMP)JPForwardInvocation) {
IMP originalForwardImp = class_replaceMethod(cls, @selector(forwardInvocation:), (IMP)JPForwardInvocation, "v@:@");
if (originalForwardImp) {
class_addMethod(cls, @selector(ORIGforwardInvocation:), originalForwardImp, "v@:@");
}
}
[cls jp_fixMethodSignature];
if (class_respondsToSelector(cls, selector)) {
NSString *originalSelectorName = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"ORIG%@", selectorName];
SEL originalSelector = NSSelectorFromString(originalSelectorName);
if(!class_respondsToSelector(cls, originalSelector)) {
class_addMethod(cls, originalSelector, originalImp, typeDescription);
}
}
NSString *JPSelectorName = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"_JP%@", selectorName];
_initJPOverideMethods(cls);
_JSOverideMethods[cls][JPSelectorName] = function;
// Replace the original secltor at last, preventing threading issus when
// the selector get called during the execution of `overrideMethod`
class_replaceMethod(cls, selector, msgForwardIMP, typeDescription);
}
JSPatch的Hook过程如下:
- 1、将
SEL(forwardInvocation)指向JSPatch的自定义转发过程IMP(JPForwardInvocation),同时再定义一个SEL(ORIGforwardInvocation),指向原来的IMP(forwardInvocation),处理原有转发。注意:对于JSPatch的每个类,尽管overrideMethod会被调用多次,但是这个步骤对于每个类只调用1次。
- 2、将
SEL(methodName)指向_objc_msgForward(_objc_msgForward_stret),同时再定义一个SEL(ORIGmethodName)指向方法原来的实现`IMP(methodName)``- 3、将替换的方法JS代码块以
_JSOverideMethods[cls][JPSelectorName] = function的形式保存下来
接下来再看下JPForwardInvocation的处理过程1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37static void JPForwardInvocation(__unsafe_unretained id assignSlf, SEL selector, NSInvocation *invocation)
{
BOOL deallocFlag = NO;
id slf = assignSlf;
NSMethodSignature *methodSignature = [invocation methodSignature];
NSInteger numberOfArguments = [methodSignature numberOfArguments];
NSString *selectorName = NSStringFromSelector(invocation.selector);
NSString *JPSelectorName = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"_JP%@", selectorName];
JSValue *jsFunc = getJSFunctionInObjectHierachy(slf, JPSelectorName);
if (!jsFunc) {
IMP invocationIMP = class_getMethodImplementation([slf class], invocation.selector);
JPExecuteORIGForwardInvocation(slf, selector, invocation);
return;
}
// 参数解析(在此不贴代码了)
...
// 执行JS代码片段,并进行返回值解析(贴一个最简单的JS代码块的执行,实际上很复杂)
JSValue *jsval; \
[_JSMethodForwardCallLock lock]; \
jsval = [jsFunc callWithArguments:params]; \
[_JSMethodForwardCallLock unlock]; \
while (![jsval isNull] && ![jsval isUndefined] && [jsval hasProperty:@"__isPerformInOC"]) { \
NSArray *args = nil; \
JSValue *cb = jsval[@"cb"]; \
if ([jsval hasProperty:@"sel"]) { \
id callRet = callSelector(![jsval[@"clsName"] isUndefined] ? [jsval[@"clsName"] toString] : nil, [jsval[@"sel"] toString], jsval[@"args"], ![jsval[@"obj"] isUndefined] ? jsval[@"obj"] : nil, NO); \
args = @[[_context[@"_formatOCToJS"] callWithArguments:callRet ? @[callRet] : _formatOCToJSList(@[_nilObj])]]; \
} \
[_JSMethodForwardCallLock lock]; \
jsval = [cb callWithArguments:args]; \
[_JSMethodForwardCallLock unlock]; \
}
...
JSPatch的原有转发逻辑1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26static void JPExecuteORIGForwardInvocation(id slf, SEL selector, NSInvocation *invocation)
{
SEL origForwardSelector = @selector(ORIGforwardInvocation:);
if ([slf respondsToSelector:origForwardSelector]) {
NSMethodSignature *methodSignature = [slf methodSignatureForSelector:origForwardSelector];
if (!methodSignature) {
_exceptionBlock([NSString stringWithFormat:@"unrecognized selector -ORIGforwardInvocation: for instance %@", slf]);
return;
}
NSInvocation *forwardInv= [NSInvocation invocationWithMethodSignature:methodSignature];
[forwardInv setTarget:slf];
[forwardInv setSelector:origForwardSelector];
[forwardInv setArgument:&invocation atIndex:2];
[forwardInv invoke];
} else {
Class superCls = [[slf class] superclass];
Method superForwardMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(superCls, @selector(forwardInvocation:));
void (*superForwardIMP)(id, SEL, NSInvocation *);
superForwardIMP = (void (*)(id, SEL, NSInvocation *))method_getImplementation(superForwardMethod);
superForwardIMP(slf, @selector(forwardInvocation:), invocation);
}
}
JSPatch hook的函数执行逻辑:
- 4、当被Hook的方法执行时,会被转发到
JPForwardInvocation函数中,该方法会把selectorName的前面拼接上”_JP”,在_JSOverideMethods中查找是否有该方法的JS代码,如果有,就进行参数解析,执行JS代码片段,最后再解析JS代码的返回值;- 5、如果未找到,说明该方法并未被JSPatch所覆盖,应该调转到
JPExecuteORIGForwardInvocation执行原有的转发- 6、如果当前类响应
origForwardSelector,则直接invoke执行;- 7、否则,寻找父类的
forwardInvocation方法,并invoke执行
用一张图表示下方法被JSPatch hook之后的状态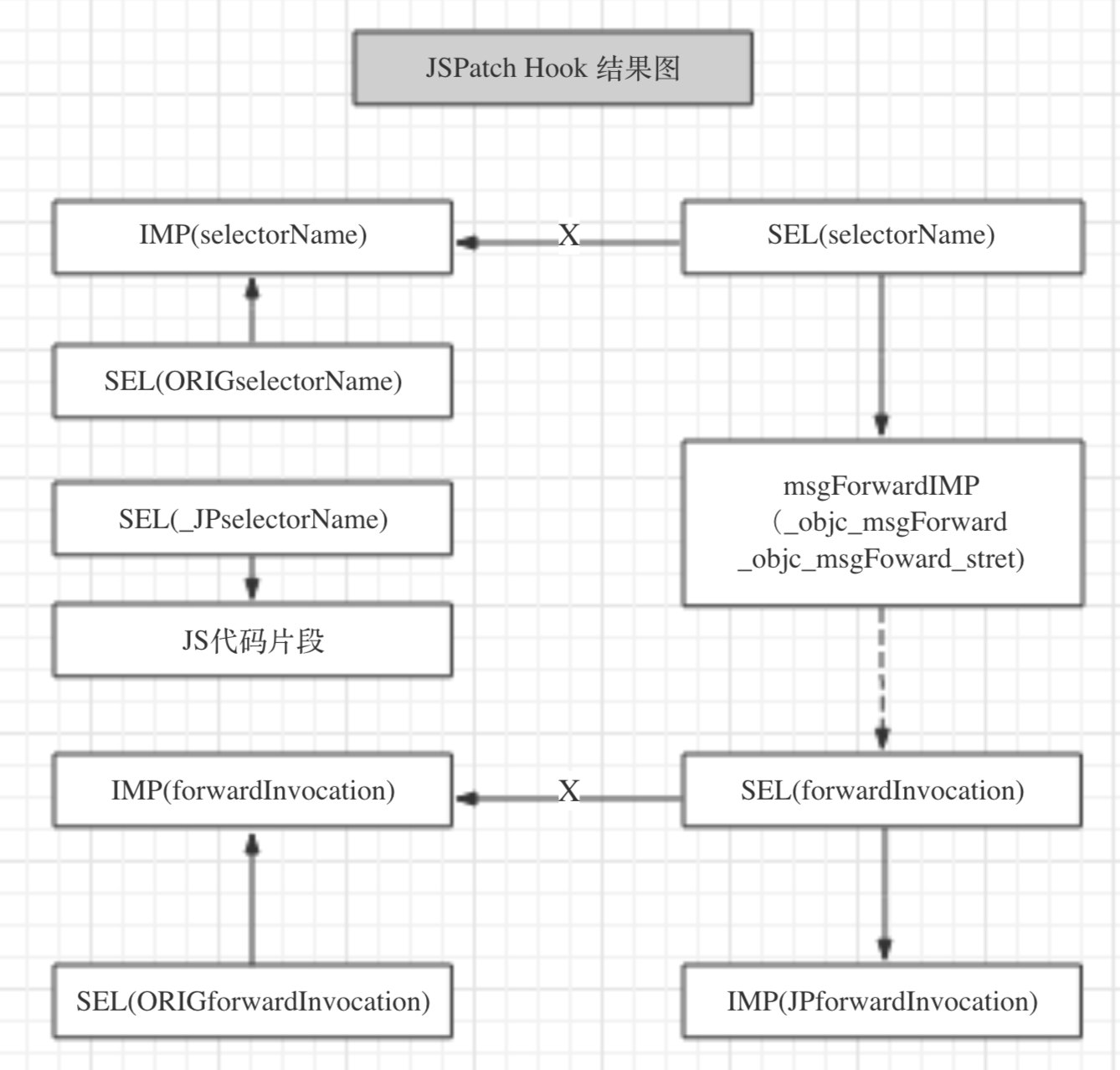
(2)Aspects的Hook原理
Aspects不光支持Hook类,还支持Hook对象,提供更小粒度的支持。对于对象的hook,
对于对象实例而言,Aspects并没有直接swizzling对象的forwardInvocation 方法,而是动态生成一个当前对象的子类,并将当前对象与子类关联,然后替换子类的 forwardInvocation方法,它的原理有些类似于KVO:将当前对象变成一个subclass 的实例,同时对于外部使用者而言,又能把它继续当成原对象在使用,而且所有的swizzling 操作都发生在子类,这样做的好处是你不需要去更改对象本身的类。但是Aspects的对象hook不在今天的讨论范围之内
我们主要讨论Aspects的类Hook
Aspects对于类的Hook与JSPatch的原理大同小异,核心代码如下:
1 | static id aspect_add(id self, SEL selector, AspectOptions options, id block, NSError **error) { |
1 | static void aspect_prepareClassAndHookSelector(NSObject *self, SEL selector, NSError **error) { |
1 | static void aspect_swizzleForwardInvocation(Class klass) { |
1 | static void __ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__(__unsafe_unretained NSObject *self, SEL selector, NSInvocation *invocation) { |
用一张图表示下方法被Aspect hook之后的状态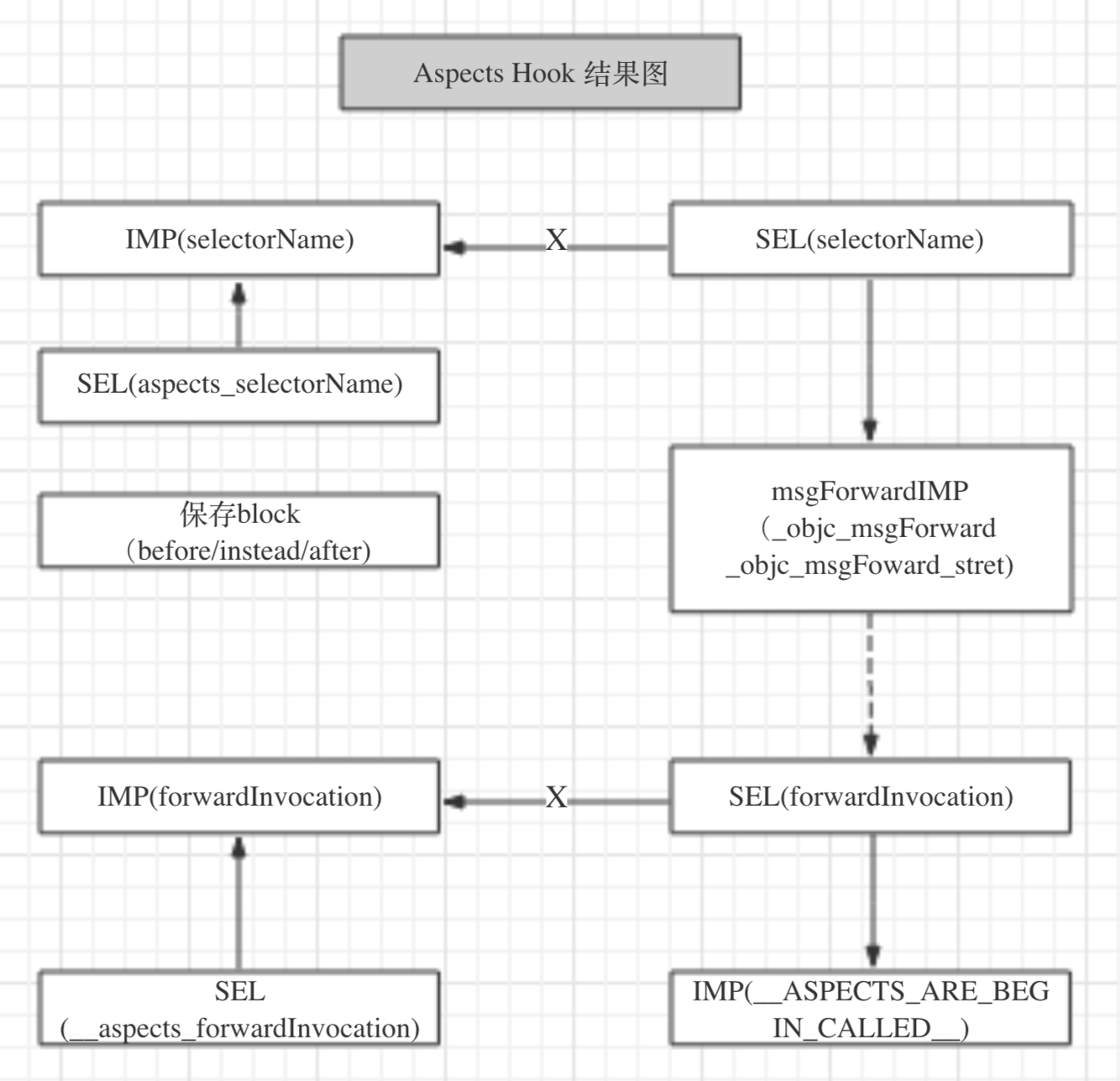
JSPatch和Aspects的Hook混战
如果项目中接入的第三方库,同时有多个库对类的forwardInvocation函数进行了Hook,那么就可能会引发各种各样的问题,接下来以Aspects和JSPatch为例,看看它俩直间的碰撞
先来点上下文
1 | @interface MyClass : NSObject |
1 | - (void)aspects_hook_test { |
1 | defineClass('MyClass', { |
先总结下遇到的问题
| 操作 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| JSPatch先hook,Aspects再hook | aspects log |
| Aspects先hook,JSPatch再hook | jspatch log |
| Aspects先hook,JSPatch再hook,且JSpatch调用了self.ORIGxxx() | crash |
| Aspects先hook父类一方法,JSPatch再hook子类同一方法,且JSPatch调用了self.super().xxx() | crash |
| JSPatch先hook父类方法,Aspects再hook子类方法,然后调用[subclass superTest] | crash |
接下来我们逐步分析:
原始状态
在没有任何hook动作之前,每个类的SEL和IMP的指向关系如下: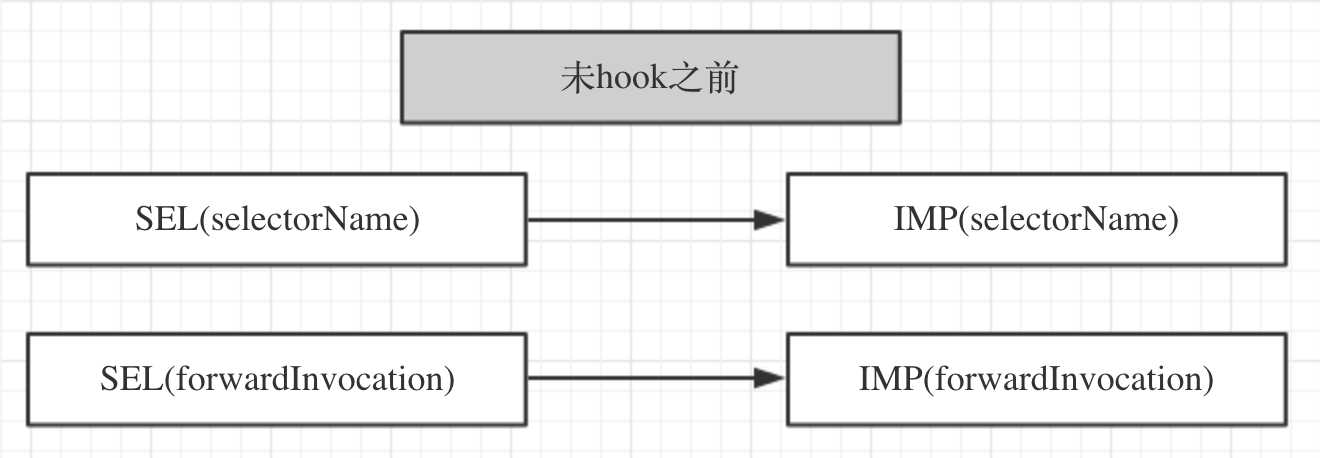
JSPatch hook
JSPatch的hook之后,类的SEL和IMP的指向示意图如下: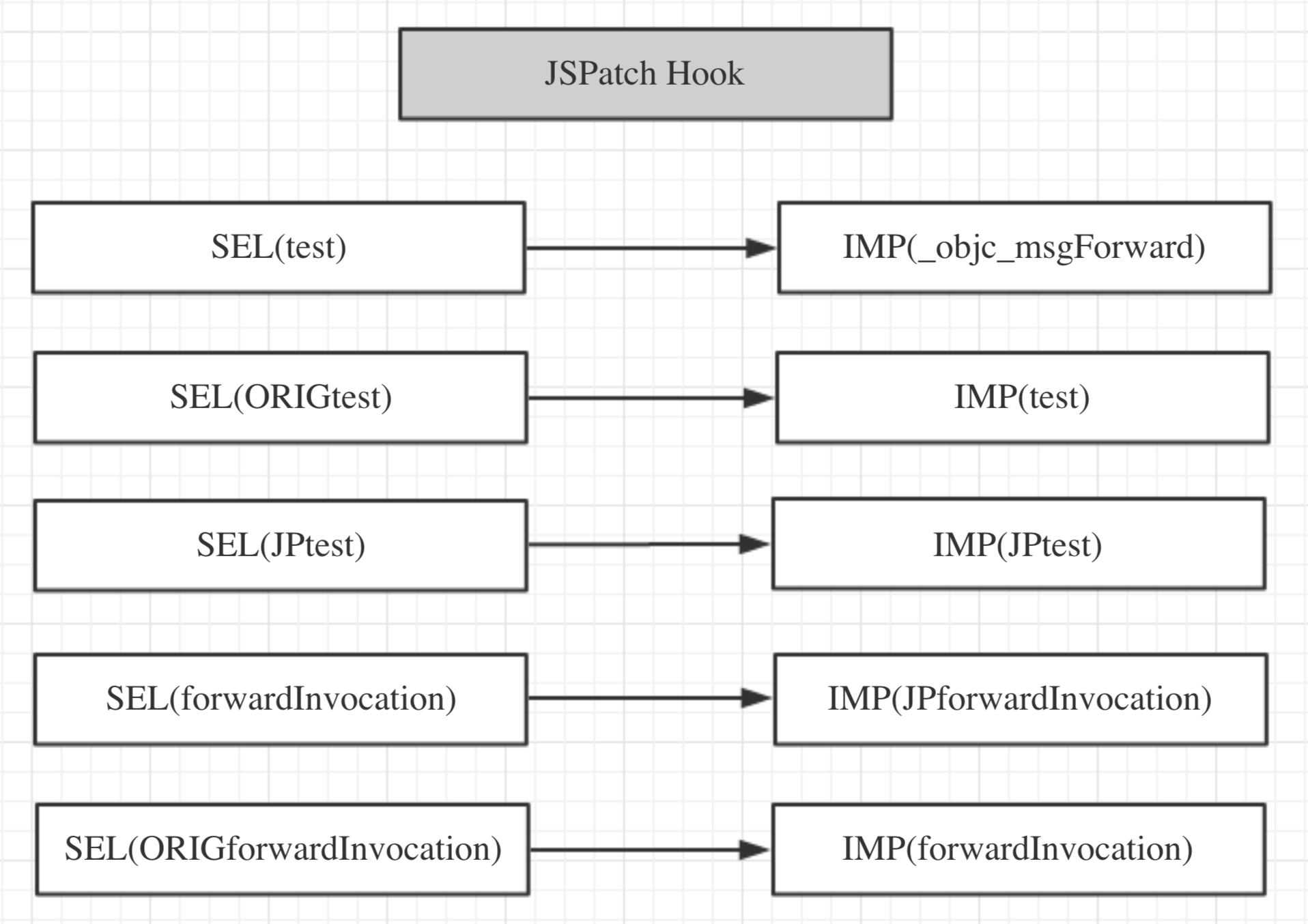
Aspects hook
Aspects的hook之后,类的SEL和IMP的指向示意图如下: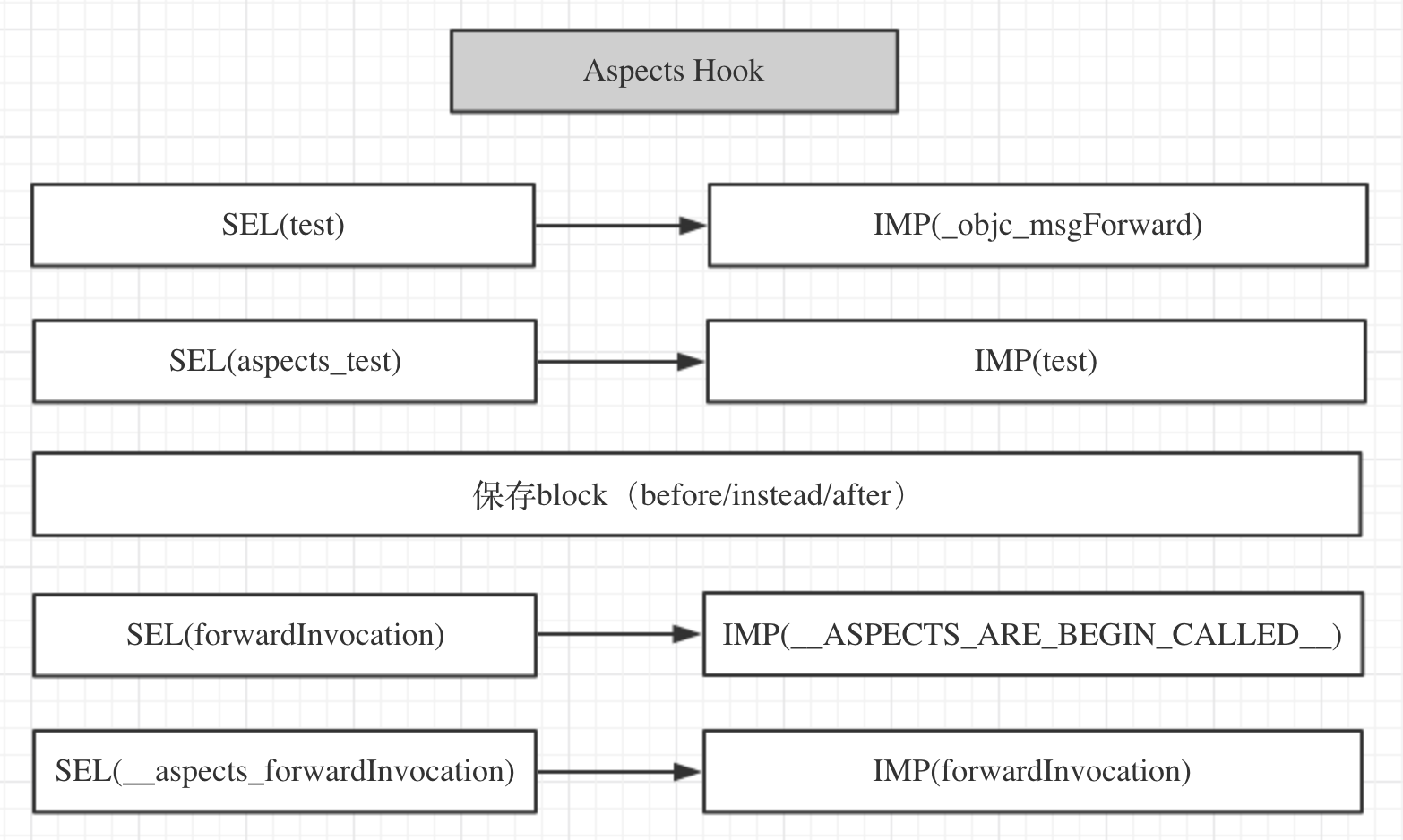
JSPatch先hook,Aspects再hook
JSPatch先hook函数test,Aspects在此基础上再对test进行hook,之后类的SEL和IMP的指向示意图如下:(注:这个时候不可避免地存在覆盖问题)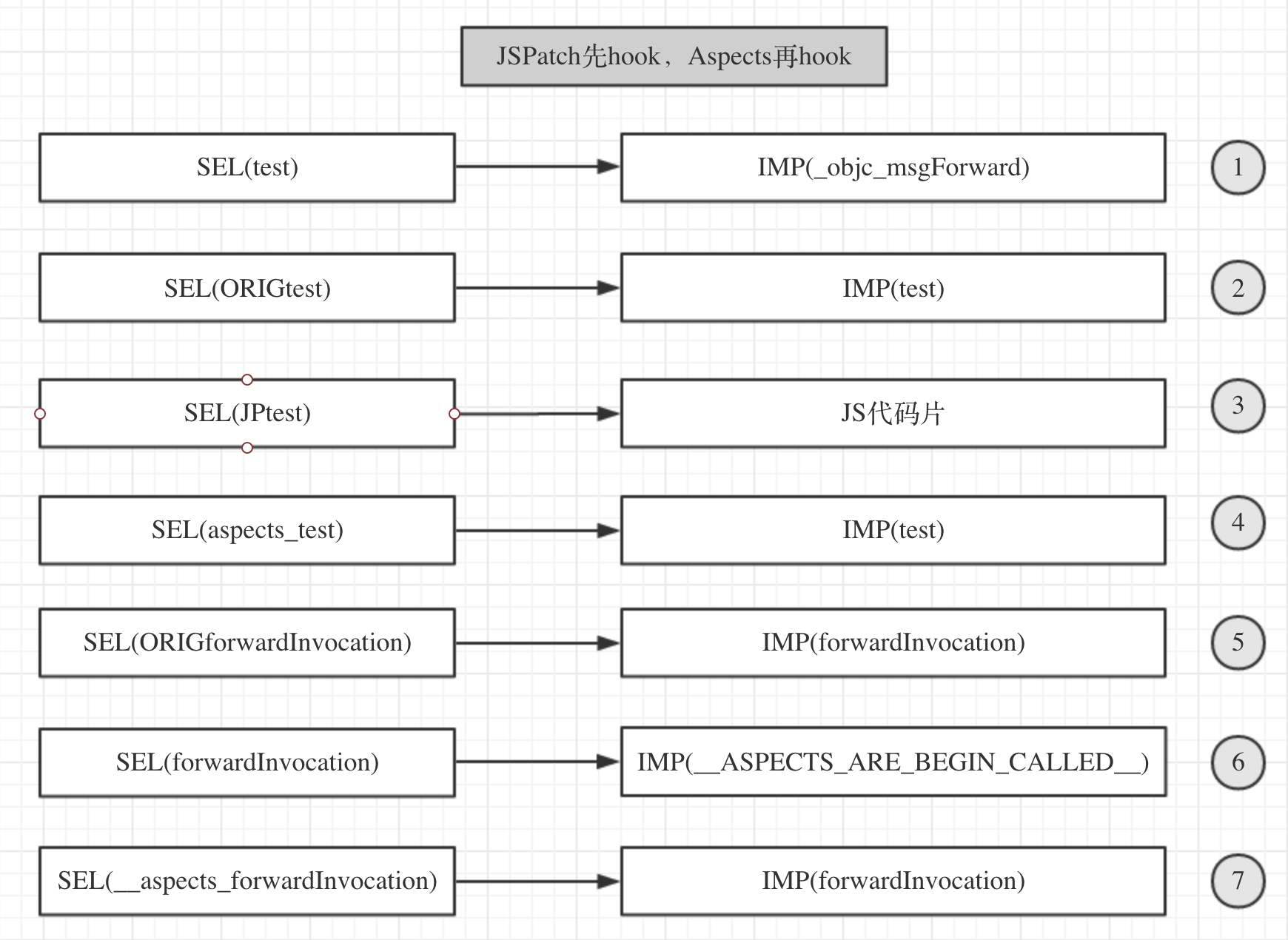
如果此时向test方法发消息,根据①的指向,理所当然会进行转发,由于此时的SEL(forwardInvocation)指向了IMP(__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__),所以转发会走到__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__函数中,由于此时能找到test对应的替换block,所以就会执行该block,输出aspects log,原先JSPatch的hook的JS代码片被覆盖,执行不到。
Aspects先hook,JSPatch再hook
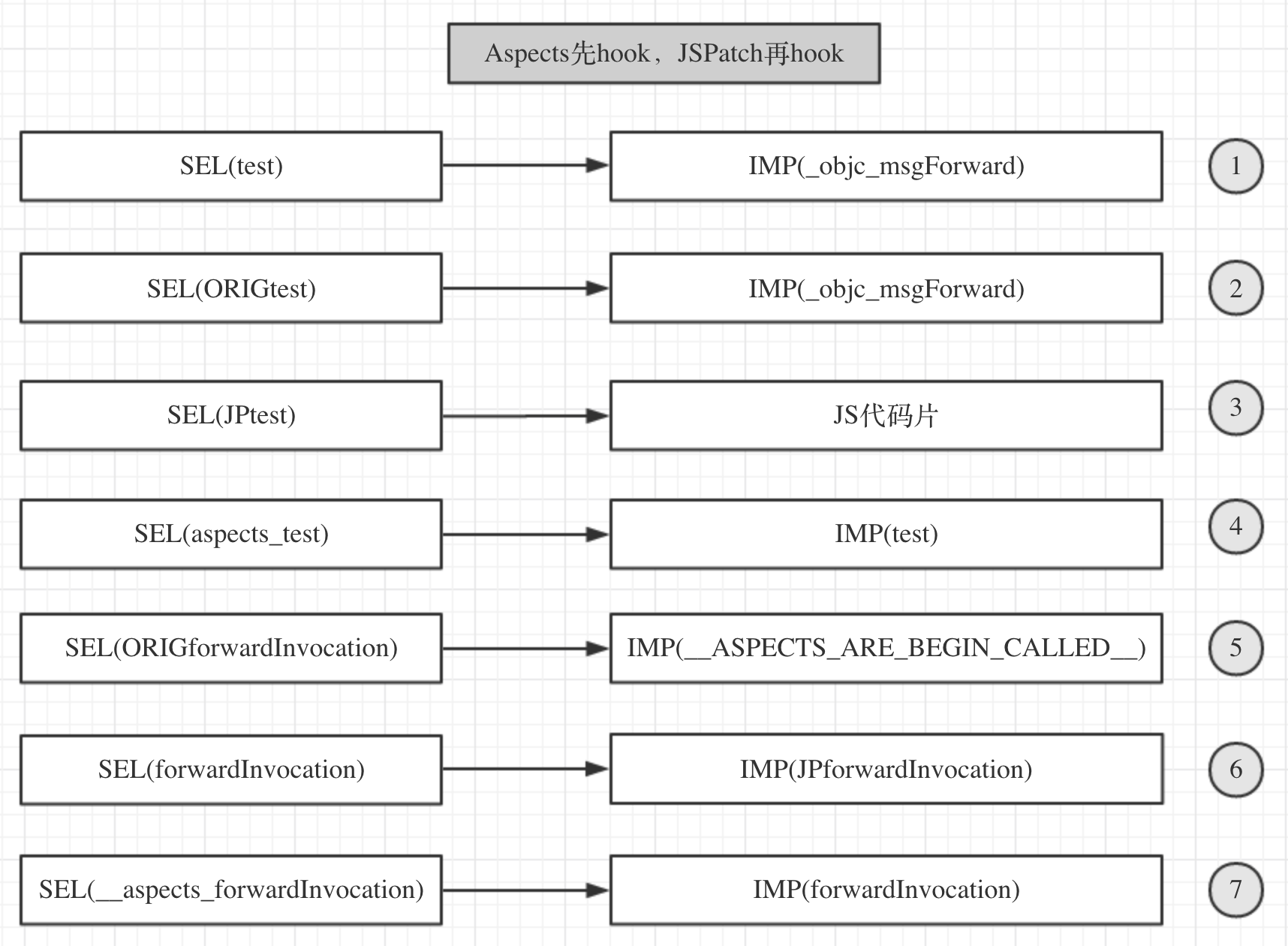
如果此时向test方法发消息,根据①的指向,理所当然会进行转发,由于此时的SEL(forwardInvocation)指向了IMP(JPforwardInvocation),所以转发会走到JPforwardInvocation函数中,由于此时能找到test对应的JS代码块,所以就会执行该JS代码块,输出jspatch log,原先Aspects的hook的block被覆盖,执行不到。
Aspects先hook,JSPatch再hook,且JSpatch调用了self.ORIGtest(),会发生crash
1 | JPAndAspects[70095:30054488] -[MyClass ORIGtest]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x60400001fa30 |

JSPatch hook的代码片如下所示,调用了self.ORIGtest()1
2
3
4
5
6defineClass('MyClass', {
test: function() {
console.log("jspatch log");
self.ORIGtest();
}
});
如果此时向test方法发消息,这个时候则会crash,为什么会crash呢?我们来分析一下:
- 根据①的指向,理所当然会进行转发,由于此时的
SEL(forwardInvocation)指向了IMP(JPforwardInvocation),所以转发会走到JPforwardInvocation函数中,由于此时能找到test对应的JS代码块,所以就会执行该JS代码块。- 在JS代码片总调用了
self.ORIGtest(),然而因为覆盖的原因,SEL(ORIGtest)不再指向IMP(test),而是指向了IMP(_objc_msgForward),毫无疑问会被转发到IMP(JPforwardInvocation)中,- 但是此时并不能找到与
_JPORIGtest对应的JS代码块,所以会走相对于JSPatch原有的转发SEL(ORIGforwardInvocation),然而此时原有的转发SEL(ORIGforwardInvocation)由于覆盖的原因,被指向了IMP(__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__),所以必然会走到函数__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__中。- 在函数
__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__中,仍然不可能找到SEL(aspects__ORIGtest)对应的block,所以会继续走相对于Aspects的原有转发SEL(__aspects_forwardInvocation),因为SEL(__aspects_forwardInvocation)指向了IMP(forwardInvocation)- 本例中我们并没有实现
IMP(forwardInvocation),所以会crash,即使我们做了实现,也仍然不可能会预料到会有这样的SEL(aspects__ORIGtest),所以也必然会crash。
那么这个问题怎么解决呢?
理论上,ORIGtest作为函数原有的实现,不应该走到转发里面,它应该是直接指向IMP(test)。然而一旦走到JPforwardInvocation里面,说明类的test方法已经被其它的库提前hook掉了。我们需要考虑当前的ORIGtest是否已经被hook,如果未hook,需要走原有的流程,如果已经被hook,需要去掉ORIG,再进行转发
修改JSPatch源代码,在函数JPForwardInvocation中,查不到对应到JS代码块并走原有转发之前,添加如下代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13if (!jsFunc) {
// 添加的代码
IMP invocationIMP = class_getMethodImplementation([slf class], invocation.selector);
if([selectorName hasPrefix:@"ORIG"] && (invocationIMP == _objc_msgForward || invocationIMP==_objc_msgForward_stret))
{
selectorName = [selectorName stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:@"ORIG" withString:@""];
invocation.selector = NSSelectorFromString(selectorName);
}
// 走原有的转发
JPExecuteORIGForwardInvocation(slf, selector, invocation);
return;
}
输出如下1
2JPAndAspects[70724:30115450] JSPatch.log: jspatch log
JPAndAspects[70724:30115450] aspects log
Aspects先hook父类test方法,JSPatch再hook子类同一方法,且JSPatch调用了self.super().xxx()
1 | @interface MyClass : NSObject |
1 | - (void)aspects_hook_test { |
1 | defineClass('MySubClass', { |
如果此时向MySubClass的一个实例对象的test方法发送消息,则会crash1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14JPAndAspects[73431:30359622] JSPatch.log: MySubClass jspatch log
JPAndAspects[73431:30359622] -[MySubClass SUPER_test]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x608000017220
JPAndAspects[73431:30359622] *** Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSInvalidArgumentException'
reason: '-[MySubClass SUPER_test]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x608000017220'
*** First throw call stack:
(
0 CoreFoundation 0x00000001044cf1ab __exceptionPreprocess + 171
1 libobjc.A.dylib 0x0000000103b64f41 objc_exception_throw + 48
2 CoreFoundation 0x000000010454fa34 -[NSObject(NSObject) doesNotRecognizeSelector:] + 132
3 JPAndAspects 0x0000000102733da1 __ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__ + 6129
4 JPAndAspects 0x0000000102752b81 JPExecuteORIGForwardInvocation + 577
5 JPAndAspects 0x000000010274442a JPForwardInvocation + 666
6 CoreFoundation 0x0000000104451e08 ___forwarding___ + 760
7 CoreFoundation 0x0000000104451a88 _CF_forwarding_prep_0 + 120
我们先来看下hook后的状态信息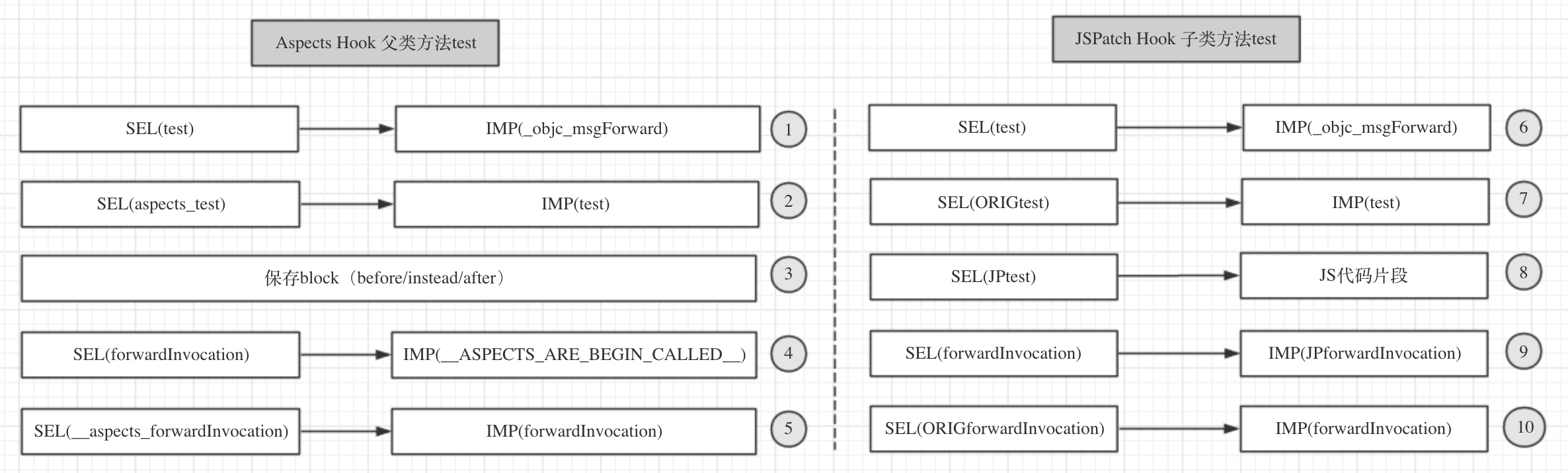
为什么会crash呢?我们来分析一下:
- 1、根据⑥的指向,如果向子类
MySubClass的一个实例对象的test方法发送消息,则会走向转发,根据⑨的指向,此时MySubClass的SEL(forwardInvocation)指向了IMP(JPforwardInvocation),肯定会转发到方法JPforwardInvocation中;- 2、由于此时能找到test对应的JS代码块,所以就会执行该JS代码块,输出
MySubClass jspatch log,由于JS代码块状中执行了self.super().test(),由于JSPatch的super的实现原理是:如果是调用super方法,找到superClass这个方法的IMP实现,为当前类新增一个方法指向super的 IMP 实现,那么调用这个类的新方法就相当于调用super方法,所以调用self.super().test()时,JSPatch会给MySubClass添加一个SEL(SUPER_test),指向父类MyClass的IMP(test),并进行转发,很不幸的是父类的SEL(test)已经指向了IMP(_objc_msgForward),所以SEL(_JPSUPER_test)也跟着指向了IMP(_objc_msgForward);- 3、根据⑨的指向,根据毫无疑问,会再次转发进入方法
JPforwardInvocation中,此时因为找不到SEL(_JPSUPER_test)对应的JS代码块,所以会进行原有转发,进入方法JPExecuteORIGForwardInvocation中- 4、由于子类
MySubClass并没有对forwardInvocation转发函数做实现,所以会进入父类MyClass的转发中,根据④的指向,肯定会跑到__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__函数中,然而在这个函数中无法找到SEL(aspects__SUPER_test)对应的block,所以会直接crash;
那么如何解决这个问题呢?
这个问题与ORIG问题很相似,理论上,super的调用也不应该跑到自己的转发中,而是直接指向父类的实现。然而由于父类被Aspects提前hook,导致对self.super().test()的调用再次阴差阳错地进入到自己的转发中,于是就发生了后来的一切。。。
继续照葫芦画瓢,在找不到对应的JS代码块进入原有转发之前,判断selectorName是否包含SUPER_前缀,并且其指向的IMP已经被hook为_objc_msgForward,如果是,需要去掉SUPER_前缀,然后再进行转发。
1 | if (!jsFunc) { |
JSPatch先hook父类方法,Aspects再hook子类方法,然后调用[subclass superTest]
1 | @interface MyClass : NSObject |
1 | @interface MySubClass : MyClass |
1 | defineClass('MyClass', { |
1 | [MySubClass aspect_hookSelector:@selector(subTest) |
1 | JPAndAspects[76443:30659220] -[MySubClass superTest]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x600000016d10 |
我们先来看下hook后的状态信息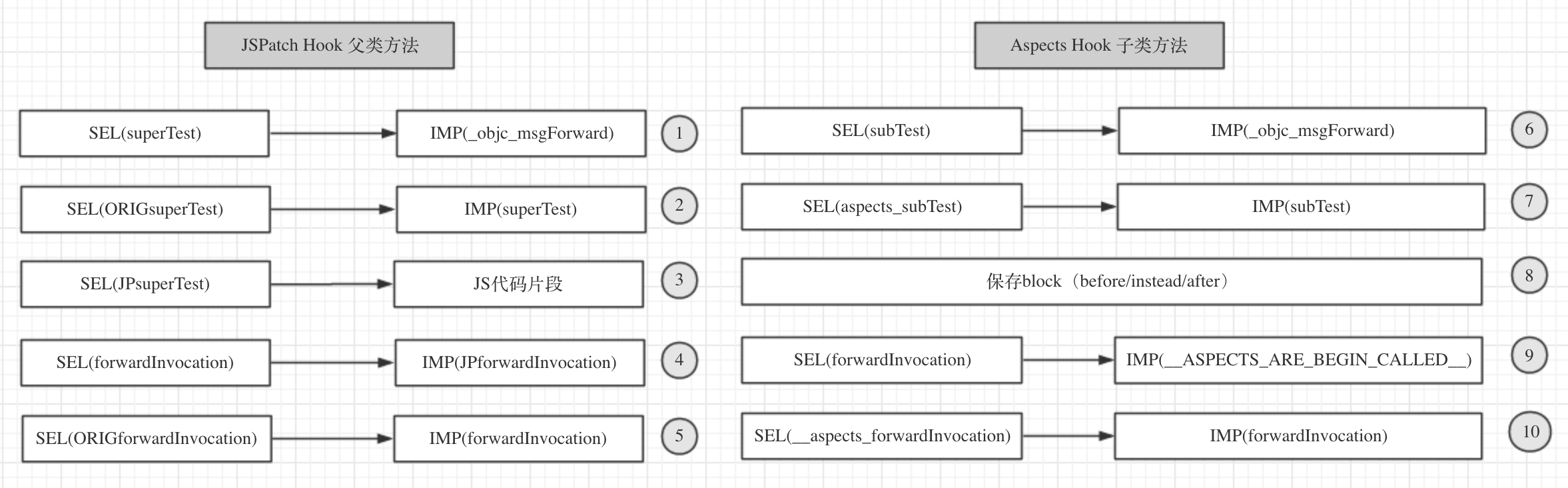
我们来分析下为什么会crash:
- 1、根据①的指向,由于父类MyClass的
SEL(superTest)指向了IMP(_objc_msgForward),所以在调用[subclass superTest],肯定会发生转发;- 2、由于子类MySubClass的
SEL(forwardInvocation)指向了IMP(__ASPECTS_ARE_BEGIN_CALLED__),所以肯定会跑到__ASPECTS_ARE_BEGIN_CALLED__函数中;- 3、由于在子类的
__ASPECTS_ARE_BEGIN_CALLED__中找不到SEL(aspects__superTest)对应的block,所以会认为没有hook,走原有的转发;- 4、由于子类本身
SEL(__aspects_forwardInvocation)指向的IMP(forwardInvocation)并没有实现,所有直接crash。
那么如何解决呢?
这个问题的本质原因是子类的处理不了SEL(aspects__superTest),同时又无法让真正可以处理的父类的forwardInvocation来处理,换句话说, forwardInvocation的继承被父类的hook和子类的hook打断了。所以解决的方案就是想办法让继承层级来处理。
修改Aspect源代码:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
// 修改前
if (!respondsToAlias) {
invocation.selector = originalSelector;
SEL originalForwardInvocationSEL = NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName);
if ([self respondsToSelector:originalForwardInvocationSEL]) {
((void( *)(id, SEL, NSInvocation *))objc_msgSend)(self, originalForwardInvocationSEL, invocation);
}else {
[self doesNotRecognizeSelector:invocation.selector];
}
}
// 修改后
if (!respondsToAlias) {
invocation.selector = originalSelector;
SEL originalForwardInvocationSEL = NSSelectorFromString(AspectsForwardInvocationSelectorName);
SEL forwardInvocationSEL = @selector(forwardInvocation:);
Class kClass = object_getClass(self);
Method method = NULL;
do{
method = class_getInstanceMethod(kClass, originalForwardInvocationSEL) ?:
class_getInstanceMethod(kClass, forwardInvocationSEL);
FORWARD_INVOCATION_IMP imp = method ? (FORWARD_INVOCATION_IMP)method_getImplementation(method) : NULL;
if(imp && (imp != &__ASPECTS_ARE_BEING_CALLED__)){
imp(self,@selector(forwardInvocation:),invocation);
break;
}
}while((kClass = class_getSuperclass(kClass)));
if(NULL == method){
[self doesNotRecognizeSelector:invocation.selector];
}
}
修改后的运行结果如下:1
JPAndAspects[78567:30830810] JSPatch.log: MyClass superTest jspatch log
如何保持正确的Hook姿势?
到目前为止,我们分析了JSPatch和Aspects同时hook消息转发forwardInvocation带来的一些问题,并逐个分析给出了解决方案,解决的核心就是要找到多个库hook之后的转发状态,从中分析方法的调用流程。
前面的混战虽然只涉及到两个库,但是其中的复杂性还是相当复杂,相信读到这里的您一定也有体会。然而这仅仅是2个库的混战,倘若有多个库呢?每个库的hook逻辑往往只考虑到了自己,认为项目中只有自己在使用黑魔法,殊不知别的库也是这么想的,由于这些库的hook肯定有前后顺序,所以必然存在逻辑覆盖或者诡异的转发跳跃,进而导致了各种各样的crash和逻辑异常:
- 1、crash肯定是我们最不想要的,所以要分析,要解决,要避免;
- 2、逻辑覆盖不一定会crash,但是对一个类同时用了好几种hook库,这种产品逻辑或者技术逻辑是否有一定的问题呢?
- 3、多个库hook出现问题的一个根本原因就是:每个库都认为自己hook之前,
SEL(forwardInvocation)指向的是原有的转发IMP(forwardInvocation),殊不知在这之前其他的库捷足先登,已经将SEL(forwardInvocation)指向了别的实现,而原来的转发实现对于当前库已经找不到了,从而导致了错误的原有转发,发生crash。如果我们实现一个获取原有转发的机制,不再依赖hook前的状态,可以解决这个问题。不过即使如此,也无法避免SEL(forwardInvocation)的指向发生逻辑覆盖,某种程度上,这个问题估计也是无解。倘若接入的库是闭源的,情况会更加严重!
所以当我们实现这样的库,或者接入这样的库,要格外小心,谨慎应对他们带来的坑!
总结
转发有风险,hook需谨慎

